What Is A Shuttle Tanker?
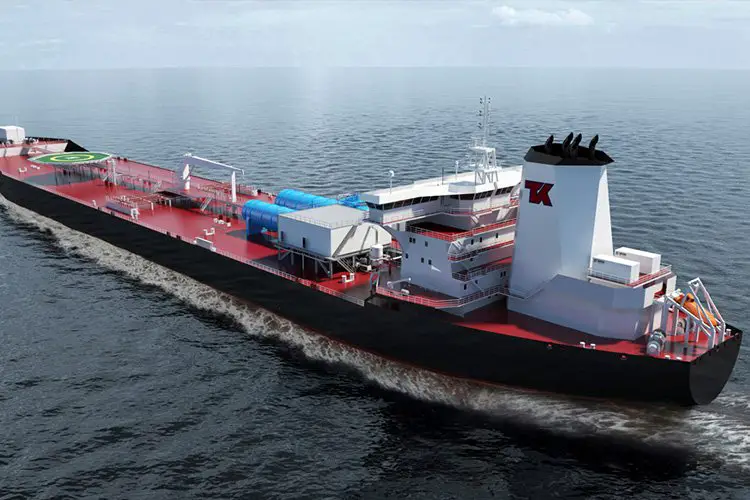

A shuttle tanker is a particular type of ship that specializes in the transportation of oil from offshore oil fields to onshore refineries. They are considered good alternatives to pipelines during inclement weather, remote areas, and in places where the depth of the water is high.
Origins Of Shuttle Tanker
Shuttle Tankers date back to the 1970s when they were first used in the North Sea. Once it came into the market, people realized its potential and started adopting it in the place of pipelines. The biggest con that the pipelines have is the fact that they need to be fixed to the receiving terminal. Shuttle tankers removed this problem and hence operators worldwide started investing in these for their flexibility when it came to both loading oil as well as transporting it to any destination.
There are some more benefits to using the shuttle tanker. It has the ability to segregate the oil. The problem with pipelines is that they often blend crude from various fields. The backup system of the shuttle tanker makes the process of maintenance a breeze. If a pipeline needs maintenance then the entire network needs to be shut down.
When it comes to safety also, shuttle tankers are ahead of conventional crude oil tankers. The latter can only be used when the waters are calm. They load from offshore installations and with the help of tugboats maintain position.
The shuttle tankers, on the other hand, are much more versatile as they can be used in all times of weather conditions and in all types of water. They come equipped with bow thrusters and stern thrusters along with dynamic positioning to help them stay in position. The low-speed maneuverability is increased with the help of flap rudders and pitch propellers.
Shuttle owners are often offered long-term contracts by field operators to offload and transport oil from the field installation to the receiving terminal. The crew receives intensive training so that they can maneuver the tanker safely when close to offshore installations. They are also required to go through high amounts of training so as to make them capable of efficiently as well as safely operating the offshore loading system and dynamic positioning of the system.
What are Dynamic Positioning Systems?
A term that we constantly come across while discussing shuttle tankers is dynamic positioning systems. They form a core part of modern shuttle tanker technology. This is what ensures that the vessel stays in position despite the inclement weather and harsh environment. This is done with the help of computers that monitors the surroundings of the vessel, like the wind, currents, tides as well as the location of the thrusters, and adjust them accordingly so as to counter their effects which might cause movement of the vessel.
Dynamic Positions are of three classes:
- The first ones have no redundancy in their computer setup. This means that if a single component fails the entire machine shuts down as there is no backup to take its place.
- DP2 vessels have redundancy. Hence if one component fails there is a backup component that can take its place. These are in high demand in places like the North Sea.
- The newer vessels come equipped with DP3. They can handle fire and flood in one compartment while keeping the system running at the same time.
Also read: What is Baltic Mooring?
Types of Systems
1. Floating production storage and offloading (FPSO)
The oil is transferred from the floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) unit. The loading system is situated on the bow of the ship enabling the shuttle to load from various platforms while at the same time maintaining safety irrespective of the weather conditions. A special cone-shaped loading system can be installed on the keel of the ship.
The loading system is connected to the offshore platform via the field export system. Depending on the safety, weather conditions, water depth, seabed conditions, and cost the type of onboard export system varies.
2. Single Point Mooring System (SPM)
SPM is an offshore loading buoy for the tankers to connect for loading and offloading of oil. An SPM is made up of the buoy, the mooring and anchoring elements, the product transfer system, and other components. They are capable of handling ships of any size and under weather conditions. It can easily position itself around the mooring point and its dynamic positioning capability prevents wear and tear to a great extent. After the positioning, the loading system and the export system are connected by a hose.
Following the introduction of the dynamic positioning in the 1980s, the Ugland Kongsberg Offshore Loading System came into the market. They were cheaper than the other options that were available and could only be used with dynamically positioned shuttle tankers.
3. Submerged Turret Loading (STL) system
Eight years later the Submerged Turret Loading (STL) system was introduced in 1993. These have submerged buoys that come through cone-shaped turrets on the keel of the shuttle tankers. Extreme weather conditions don’t create any problem for them as long as the sea state does not cause 6 meters.
4. Single Anchor Loading (SAL)
For good weather conditions and shallow waters, the Single Anchor Loading (SAL) is used. They were introduced in the late 1990s. Their popularity is due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness when compared to STL.
5. Tandem Loading System
The Tandem Loading System was first carried out back in 1991. It required the shuttle tanker to be connected to the stern of the FPSO or FSO. Dynamic positioning is needed to monitor the position of the two units.
Photo credit: dnvgl.com







I can see how a business could really benefit from getting the right loading for their barge to make sure that they can get their products delivered safely. Making sure that she can get some help from a professional could allow them to have better organization. It was interesting to learn about how they can be a lot safer while unloading things to different platforms during different weather conditions.